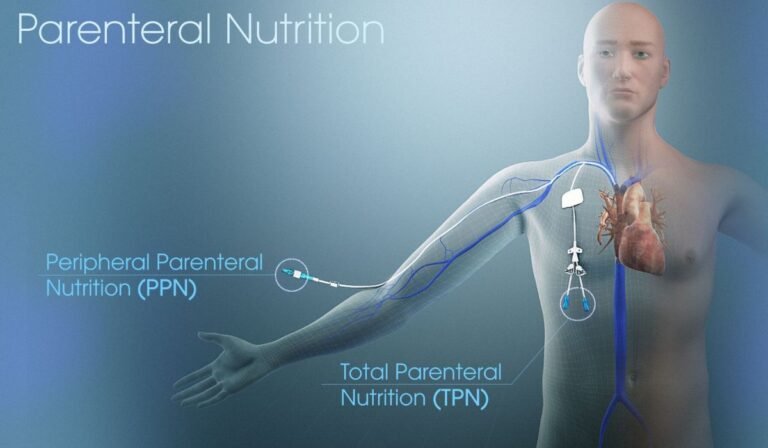
The Essentials of TPN
Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) is a lifesaving therapy for patients who cannot absorb nutrition through their digestive tract. TPN bypasses the gut entirely, whether due to bowel disease, surgery, or severe malfunction. It supplies critical nutrients—like protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals—through a vein, typically via a central line. This approach ensures that people unable to eat or digest normally receive the sustenance their bodies require to heal, grow, or maintain daily functions.
Many individuals, including children and adults, now opt for TPN nutrition at home as an alternative to long hospitalizations. Advancements in equipment, sterile solutions, and delivery methods have made it possible to maintain a high quality of health—and life—outside of clinical settings, even for those with complex medical needs.
The Process of TPN Administration
TPN is delivered through a small, flexible catheter inserted into a large vein—commonly in the chest area. This allows concentrated nutrition to enter the bloodstream, offering rapid and efficient delivery. The process is carefully timed and controlled, often administered several hours daily. Healthcare providers personalize home TPN regimens to accommodate the patient’s routines, lifestyle, and medical requirements.
Each infusion setup requires precise preparation, including cleansing hands, disinfecting the catheter site, and monitoring for complications. Training is essential so patients and caregivers understand how to prevent infection and troubleshoot equipment issues, maximizing the safety and effectiveness of TPN therapy.
Key Components of TPN Solutions
Every TPN solution is tailor-made. It contains a calculated balance of macronutrients and micronutrients: amino acids for building proteins, glucose for energy, lipids for essential fats, plus electrolytes such as potassium and sodium. Vitamins and trace minerals are added to prevent deficiencies. These nutrients are chosen for short-term needs and ongoing maintenance, tailored as lab results or symptoms change.
Adjustments to the mixture are made based on regular blood work and the patient’s overall clinical condition. This customization helps meet specific metabolic demands and mitigates risks of imbalances, making coordinated, informed oversight critical.
Transitioning to Home-Based TPN
Moving TPN therapy from the hospital to home involves detailed planning, training, and ongoing adjustment. Patients and caregivers are taught sterile techniques for handling catheters, pump operation, and recognizing warning signs of infection or metabolic issues. Emotional support is also crucial during this transition, as many face apprehension about managing complex care away from medical teams.
According to insights from the National Institutes of Health, families receiving comprehensive training and easy access to expert advice at home continue to report better outcomes, fewer complications, and improved quality of life.
Overcoming Challenges With TPN
Common challenges with TPN therapy include catheter infections, metabolic disturbances, and emotional fatigue from the daily regimen. Accessing reliable resources for ongoing education and psychosocial support helps reduce anxiety and risk. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention offers practical resources for nutrition safety, wellness strategies, and managing possible side effects.
Regular communication with healthcare professionals aids in quickly identifying and resolving complications, helping to maintain confidence and consistency in care.
Tips for Successful TPN Management
Home infusion therapy requires clinical precision and personal consistency to ensure safety and comfort.
- Establish a daily routine for setup and infusion to prevent errors and foster peace of mind.
- Keep supplies organized and easily accessible to minimize stress during busy times.
- Track symptoms, catheter care, and lab results in a log or digital app to detect changes earlier.
- Leverage community forums or local support groups for shared experiences and emotional support.
These small, intentional habits can make a big difference in maintaining treatment effectiveness and emotional well-being.
The Ongoing Role of Healthcare Professionals
Strong relationships with doctors, dietitians, pharmacists, and nurses are critical throughout TPN therapy. These professionals review lab work, adjust nutrient formulas, and provide guidance regarding any changes or concerns. Telehealth and quick messaging platforms allow for more frequent, convenient check-ins, supporting patient safety and resolving issues before they escalate. Keeping all medical records, supply lists, and provider contacts organized streamlines communication and ensures emergency readiness.
Advances and the Future of TPN Therapy
Technology and formula design improvements continue to make TPN therapy safer and easier to manage at home. Smarter pumps, better sterilization procedures, and enhanced support networks foster greater independence for people who rely on this therapy. Ongoing research also focuses on preventing complications and improving long-term outcomes, empowering more families to embrace home-based TPN with renewed optimism confidently.